Table of Contents
Compactor #
The thanos compact command applies the compaction procedure of the Prometheus 2.0 storage engine to block data stored in object storage. It is generally not semantically concurrency safe and must be deployed as a singleton against a bucket.
Compactor is also responsible for downsampling of data. There is a time delay before downsampling at a given resolution is possible. This is necessary because downsampled chunks will have fewer samples in them, and as chunks are fixed size, data spanning more time will be required to fill them.
- Creating 5m downsampling for blocks older than 40 hours (2d)
- Creating 1h downsampling for blocks older than 10 days (2w)
Example:
thanos compact --data-dir /tmp/thanos-compact --objstore.config-file=bucket.yml
Example content of bucket.yml:
type: GCS
config:
bucket: example-bucket
By default, thanos compact will run to completion which makes it possible to execute it as a cronjob. Using the arguments --wait and --wait-interval=5m it’s possible to keep it running.
Compactor, Sidecar, Receive and Ruler are the only Thanos components which should have write access to object storage, with only Compactor being able to delete data.
NOTE: High availability for Compactor is generally not required. See the Availability section.
Compaction #
The Compactor, among other things, is responsible for compacting multiple blocks into one.
Why even compact? This is a process, also done by Prometheus, to reduce the number of blocks and compact index indices. We can compact an index quite well in most cases, because series usually live longer than the duration of the smallest blocks (2 hours).
Compaction Groups / Block Streams #
Usually those blocks come through the same source. We call blocks from a single source a “stream” of blocks or “compaction group”. We distinguish streams by external labels. Blocks with the same labels are considered as produced by the same source.
This is because external_labels are added by the Prometheus instance which produced the block.
⚠ This is why those labels on block must be both unique and persistent across different Prometheus instances. ⚠
- By unique, we mean that the set of labels in a Prometheus instance must be different from all other sets of labels of your Prometheus instances, so that the compactor will be able to group blocks by Prometheus instance.
- By persistent, we mean that one Prometheus instance must keep the same labels if it restarts, so that the compactor will keep compacting blocks from an instance even when a Prometheus instance goes down for some time.
Natively Prometheus does not store external labels anywhere. This is why external labels are added only on upload time to the ThanosMeta section of meta.json in each block.
NOTE: In default mode the state of two or more blocks having the same external labels and overlapping in time is assumed as an unhealthy situation. Refer to Overlap Issue Troubleshooting for more info. This results in compactor halting.
Warning: Only one instance of Compactor may run against a single stream of blocks in a single object storage. #
⚠️ ⚠️ ⚠️
Because not all object storage providers implement a safe locking mechanism, you need to ensure on your own that only a single Compactor is running against a single stream of blocks on a single bucket. Running more than one Compactor may result in Overlap Issues which have to be resolved manually.
This rule also means that there could be a problem when both compacted and non-compacted blocks are being uploaded by a sidecar. This is why the “upload compacted” function still lives under a separate --shipper.upload-compacted flag that helps to ensure that compacted blocks are uploaded before anything else. The singleton rule is also why local Prometheus compaction has to be disabled in order to use Thanos Sidecar with the upload option. Use - at your own risk! - the hidden --shipper.ignore-unequal-block-size flag to disable this check.
NOTE: In future versions of Thanos it’s possible that both restrictions will be removed once vertical compaction reaches production status.
You can though run multiple Compactors against a single Bucket as long as each instance compacts a separate stream of blocks. You can do this in order to scale the compaction process.
Vertical Compactions #
Thanos and Prometheus support vertical compaction, the process of compacting multiple streams of blocks into one.
In Prometheus, this can be triggered by setting a hidden flag in Prometheus and putting additional TSDB blocks in Prometheus’ local data directory. Extra blocks can overlap with existing ones. When Prometheus detects this situation, it performs vertical compaction which compacts overlapping blocks into a single one. This is mainly used for backfilling.
In Thanos, this works similarly, but on a bigger scale and using external labels for grouping as explained in the “Compaction” section.
In both systems, series with the same labels are merged together. In Prometheus, merging samples is naive. It works by deduplicating samples within exactly the same timestamps. Otherwise samples are merged and sorted by timestamp. Thanos also supports a new penalty based samples merging strategy, which is explained in Deduplication.
NOTE: Both Prometheus’ and Thanos’ default behaviour is to fail compaction if any overlapping blocks are spotted. (For Thanos, with the same external labels).
Vertical Compaction Use Cases #
The following are valid use cases for vertical compaction:
- Races between multiple compactions, for example multiple Thanos compactors or between Thanos and Prometheus compactions. While this will cause extra computational overhead for Compactor it’s safe to enable vertical compaction for this case.
- Backfilling. If you want to add blocks of data to any stream where there already is existing data for some time range, you will need to enable vertical compaction.
- Offline deduplication of series. It’s very common to have the same data replicated into multiple streams. We can distinguish two common strategies for deduplications,
one-to-oneandpenalty:one-to-onededuplication is when multiple series (with the same labels) from different blocks for the same time range have exactly the same samples: Same values and timestamps. This is very common when using Receivers with replication greater than 1 as receiver replication copies samples exactly (same timestamps and values) to different receive instances.penaltydeduplication is when the same data is duplicated logically, i.e. the same application is scraped from two different Prometheis. This usually requires more complex deduplication algorithms. For example, one that is used to deduplicate on the fly on the Querier. This is a common case when Prometheus HA replicas are used. You can enable this deduplication strategy via the--deduplication.func=penaltyflag.
Vertical Compaction Risks #
The main risk is the irreversible implications of potential configuration errors:
- If you accidentally upload blocks with the same external labels but produced by totally different Prometheis for totally different applications, some metrics can overlap and potentially merge together, making the series useless.
- If you merge disjoint series in multiple of blocks together, there is currently no easy way to split them back.
- The
penaltyoffline deduplication algorithm has its own limitations. Even though it has been battle-tested for quite a long time, very few issues still come up from time to time (such as breaking rate/irate). If you’d like to enable this deduplication algorithm, do so at your own risk and back up your data first!
Enabling Vertical Compaction #
NOTE: See the “risks” section to understand the implications and experimental nature of this feature.
You can enable vertical compaction using the hidden flag --compact.enable-vertical-compaction
If you want to “virtually” group blocks differently for deduplication use cases, use --deduplication.replica-label=LABEL to set one or more labels to be ignored during block loading.
For example if you have following set of block streams:
external_labels: {cluster="eu1", replica="1", receive="true", environment="production"}
external_labels: {cluster="eu1", replica="2", receive="true", environment="production"}
external_labels: {cluster="us1", replica="1", receive="true", environment="production"}
external_labels: {cluster="us1", replica="1", receive="true", environment="staging"}
and set --deduplication.replica-label="replica", Compactor will assume those as:
external_labels: {cluster="eu1", receive="true", environment="production"} (2 streams, resulted in one)
external_labels: {cluster="us1", receive="true", environment="production"}
external_labels: {cluster="us1", receive="true", environment="staging"}
On the next compaction, multiple streams’ blocks will be compacted into one.
If you need a different deduplication algorithm, use --deduplication.func=FUNC flag. The default value is the original one-to-one deduplication.
Enforcing Retention of Data #
By default, there is NO retention set for object storage data. This means that you store data forever, which is a valid and recommended way of running Thanos.
You can configure retention by using --retention.resolution-raw --retention.resolution-5m and --retention.resolution-1h flag. Not setting them or setting to 0s means no retention.
NOTE: ⚠ ️Retention is applied right after Compaction and Downsampling loops. If those are failing, data will never be deleted.
Downsampling #
Downsampling is a process of rewriting series’ to reduce overall resolution of the samples without losing accuracy over longer time ranges.
To learn more see video from KubeCon 2019
TL;DR on how thanos downsampling works #
Thanos Compactor takes “raw” resolution block and creates a new one with “downsampled” chunks. Downsampled chunk takes on storage level form of “AggrChunk”:
message AggrChunk {
int64 min_time = 1;
int64 max_time = 2;
Chunk raw = 3;
Chunk count = 4;
Chunk sum = 5;
Chunk min = 6;
Chunk max = 7;
Chunk counter = 8;
}
This means that for each series we collect various aggregations with a given interval: 5m or 1h (depending on resolution). This allows us to keep precision on large duration queries, without fetching too many samples.
⚠ ️Downsampling: Note About Resolution and Retention ⚠️ #
Resolution is a distance between data points on your graphs. E.g.
raw- the same as scrape interval at the moment of data ingestion5 minutes- data point is every 5 minutes1 hour- data point is every 1h
Compactor downsampling is done in two passes:
- All raw resolution metrics that are older than 40 hours are downsampled at a 5m resolution
- All 5m resolution metrics older than 10 days are downsampled at a 1h resolution
NOTE: If retention at each resolution is lower than minimum age for the successive downsampling pass, data will be deleted before downsampling can be completed. As a rule of thumb retention for each downsampling level should be the same, and should be greater than the maximum date range (10 days for 5m to 1h downsampling).
Keep in mind that the initial goal of downsampling is not saving disk or object storage space. In fact, downsampling doesn’t save you any space but instead, it adds 2 more blocks for each raw block which are only slightly smaller or relatively similar size to raw blocks. This is done by internal downsampling implementation which, to ensure mathematical correctness, holds various aggregations. This means that downsampling can increase the size of your storage a bit (~3x), if you choose to store all resolutions (recommended and enabled by default).
The goal of downsampling is to provide an opportunity to get fast results for range queries of big time intervals like months or years. In other words, if you set --retention.resolution-raw less than --retention.resolution-5m and --retention.resolution-1h - you might run into a problem of not being able to “zoom in” to your historical data.
To avoid confusion - you might want to think about raw data as a “zoom in” opportunity. Considering the values for mentioned options - always think “Will I need to zoom in to the day 1 year ago?” if the answer is “yes” - you most likely want to keep raw data for as long as 1h and 5m resolution, otherwise you’ll be able to see only a downsampled representation of how your raw data looked like.
There’s also a case when you might want to disable downsampling at all with --downsampling.disable. You might want to do it when you know for sure that you are not going to request long ranges of data (obviously, because without downsampling those requests are going to be much much more expensive than with it). A valid example of that case is when you only care about the last couple weeks of your data or use it only for alerting, but if that’s your case - you also need to ask yourself if you want to introduce Thanos at all instead of just vanilla Prometheus?
Ideally, you will have an equal retention set (or no retention at all) to all resolutions which allow both “zoom in” capabilities as well as performant long ranges queries. Since object storages are usually quite cheap, storage size might not matter that much, unless your goal with thanos is somewhat very specific and you know exactly what you’re doing.
Not setting this flag, or setting it to 0d, i.e. --retention.resolution-X=0d, will mean that samples at the X resolution level will be kept forever.
Please note that blocks are only deleted after they completely “fall off” of the specified retention policy. In other words, the “max time” of a block needs to be older than the amount of time you had specified.
Deleting Aborted Partial Uploads #
It can happen that a producer started uploading some block, but it never finished and it never will. Sidecars will retry in case of failures during upload or process (unless there was no persistent storage), but a very common case is with Compactor. If the Compactor process crashes during upload of a compacted block, the whole compaction starts from scratch and a new block ID is created. This means that partial upload will never be retried.
To handle this case there is the --delete-delay=48h flag that starts deletion of directories inside object storage without meta.json only after a given time.
This value has to be smaller than upload duration and consistency delay.
Halting #
Because of the very specific nature of Compactor which is writing to object storage, potentially deleting sensitive data, and downloading GBs of data, by default we halt Compactor on certain data failures. This means that Compactor does not crash on halt errors, but instead keeps running and does nothing with metric thanos_compact_halted set to 1.
Reason is that we don’t want to retry compaction and all the computations if we know that, for example, there is already an overlapped state in the object storage for some reason.
Hidden flag --no-debug.halt-on-error controls this behavior. If set, on halt error Compactor exits.
Resources #
CPU #
It’s recommended to give --compact.concurrency amount of CPU cores.
Memory #
Memory usage depends on block sizes in the object storage and compaction concurrency.
Generally, the maximum memory utilization is exactly the same as for Prometheus for compaction process:
- For each source block considered for compaction:
- 1/32 of all block’s symbols
- 1/32 of all block’s posting offsets
- Single series with all labels and all chunks.
You need to multiply this with X where X is --compact.concurrency (by default 1).
NOTE: Don’t check heap memory only. Prometheus and Thanos compaction leverages mmap heavily which is outside of Go runtime stats. Refer to process / OS memory used rather. On Linux/MacOS Go will also use as much as available, so utilization will be always near limit.
Generally, for a medium-sized bucket, a limit of 10GB of memory should be enough to keep it working.
Network #
Overall, Compactor is the component that can potentially use the highest amount of network bandwidth, so place it near the bucket’s zone/location.
It has to download each block needed for compaction / downsampling and it does that on every compaction / downsampling. It then uploads computed blocks. It also refreshes the state of bucket often.
Disk #
The compactor needs local disk space to store intermediate data for its processing as well as bucket state cache. Generally, for medium sized bucket about 100GB should be enough to keep working as the compacted time ranges grow over time. However, this highly depends on size of the blocks. In worst case scenario compactor has to have space adequate to 2 times 2 weeks (if your maximum compaction level is 2 weeks) worth of smaller blocks to perform compaction. First, to download all of those source blocks, second to build on disk output of 2 week block composed of those smaller ones.
You need to multiply this with X where X is --compact.concurrency (by default 1).
On-disk data is safe to delete between restarts and should be the first attempt to get crash-looping compactors unstuck. However, it’s recommended to give the Compactor persistent disk in order to effectively use bucket state cache between restarts.
Availability #
Compactor, generally, does not need to be highly available. Compactions are needed from time to time, only when new blocks appear.
The only risk is that without compactor running for longer time (weeks) you might see reduced performance of your read path due to amount of small blocks, lack of downsampled data and retention not enforced
Scalability #
The main and only Service Level Indicator for Compactor is how fast it can cope with uploaded TSDB blocks to the bucket.
To understand that you can use mix thanos_objstore_bucket_last_successful_upload_time being quite fresh, thanos_compact_halted being non 1 and thanos_blocks_meta_synced{state="loaded"} constantly increasing over days.
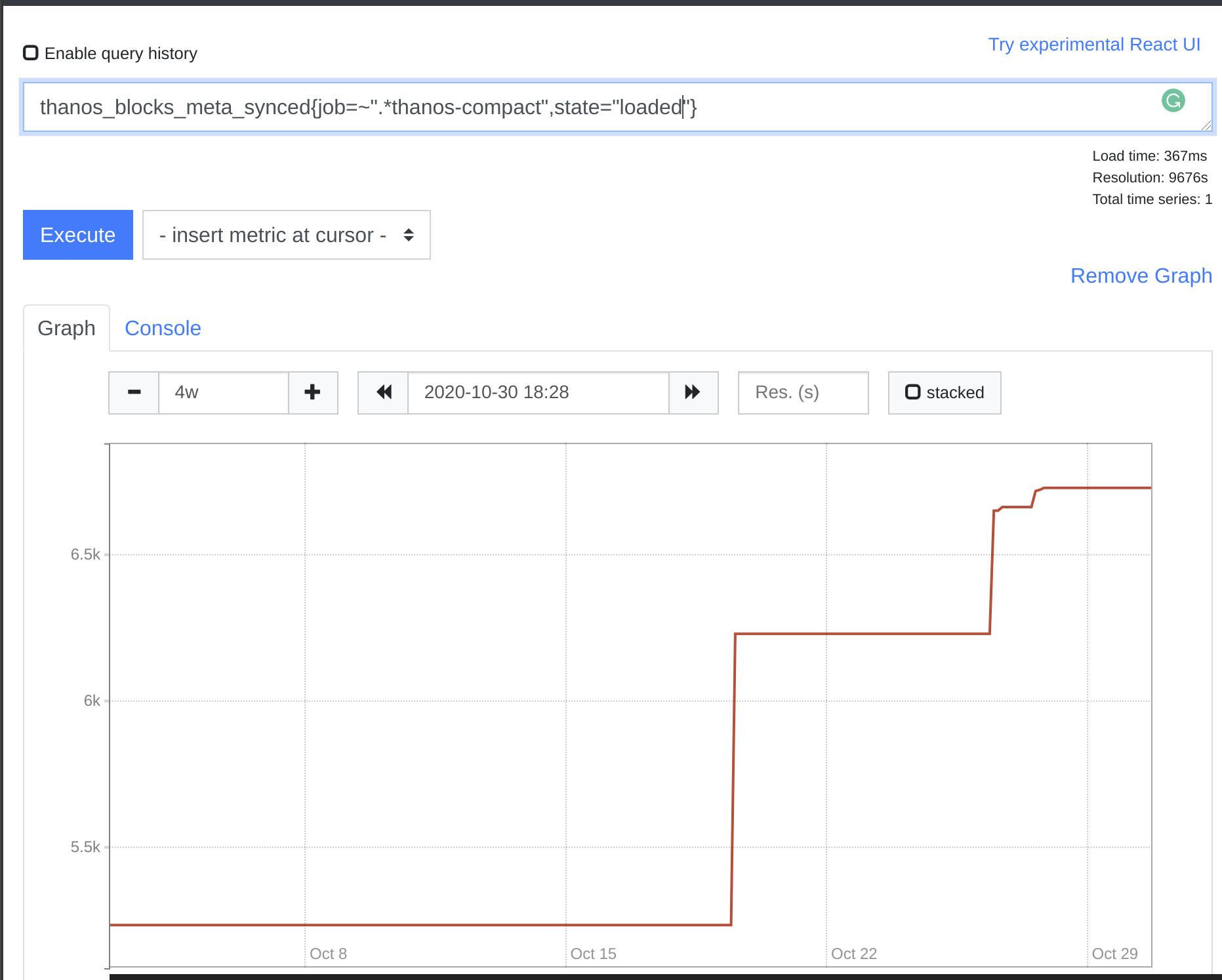
Generally there two scalability directions:
- Too many producers/sources (e.g Prometheus-es) are uploading to same object storage. Too many “streams” of work for Compactor. Compactor has to scale with the number of producers in the bucket.
You should horizontally scale Compactor to cope with this using label sharding. This allows to assign multiple streams to each instance of compactor.
- TSDB blocks from single stream is too big, it takes too much time or resources.
This is rare as first you would need to ingest that amount of data into Prometheus and it’s usually not recommended to have bigger than 10 millions series in the 2 hours blocks. However, with 2 weeks blocks, potential Vertical Compaction enabled and other producers than Prometheus (e.g backfilling) this scalability concern can appear as well. See Limit size of blocks ticket to track progress of solution if you are hitting this.
Eventual Consistency #
Depending on the Object Storage provider like S3, GCS, Ceph etc; we can divide the storages into strongly consistent or eventually consistent. Since there are no consistency guarantees provided by some Object Storage providers, we have to make sure that we have a consistent lock-free way of dealing with Object Storage irrespective of the choice of object storage.
Consistency Delay #
In order to make sure we don’t read partially uploaded block (or eventually visible fully in system) we established --consistency-delay=30m delay for all components reading blocks.
This means that blocks are visible / loadable for compactor (and used for retention, compaction planning, etc), only after 30m from block upload start in object storage.
Block Deletions #
In order to achieve co-ordination between compactor and all object storage readers without any race, blocks are not deleted directly. Instead, blocks are marked for deletion by uploading deletion-mark.json file for the block that was chosen to be deleted. This file contains unix time of when the block was marked for deletion.
Flags #
usage: thanos compact [<flags>]
Continuously compacts blocks in an object store bucket.
Flags:
--auto-gomemlimit.ratio=0.9
The ratio of reserved GOMEMLIMIT memory to the
detected maximum container or system memory.
--block-discovery-strategy="concurrent"
One of concurrent, recursive. When set to
concurrent, stores will concurrently issue
one call per directory to discover active
blocks in the bucket. The recursive strategy
iterates through all objects in the bucket,
recursively traversing into each directory.
This avoids N+1 calls at the expense of having
slower bucket iterations.
--block-files-concurrency=1
Number of goroutines to use when
fetching/uploading block files from object
storage.
--block-meta-fetch-concurrency=32
Number of goroutines to use when fetching block
metadata from object storage.
--block-viewer.global.sync-block-interval=1m
Repeat interval for syncing the blocks between
local and remote view for /global Block Viewer
UI.
--block-viewer.global.sync-block-timeout=5m
Maximum time for syncing the blocks between
local and remote view for /global Block Viewer
UI.
--bucket-web-label=BUCKET-WEB-LABEL
External block label to use as group title in
the bucket web UI
--compact.blocks-fetch-concurrency=1
Number of goroutines to use when download block
during compaction.
--compact.cleanup-interval=5m
How often we should clean up partially uploaded
blocks and blocks with deletion mark in the
background when --wait has been enabled. Setting
it to "0s" disables it - the cleaning will only
happen at the end of an iteration.
--compact.concurrency=1 Number of goroutines to use when compacting
groups.
--compact.progress-interval=5m
Frequency of calculating the compaction progress
in the background when --wait has been enabled.
Setting it to "0s" disables it. Now compaction,
downsampling and retention progress are
supported.
--consistency-delay=30m Minimum age of fresh (non-compacted)
blocks before they are being processed.
Malformed blocks older than the maximum of
consistency-delay and 48h0m0s will be removed.
--data-dir="./data" Data directory in which to cache blocks and
process compactions.
--deduplication.func= Experimental. Deduplication algorithm for
merging overlapping blocks. Possible values are:
"", "penalty". If no value is specified,
the default compact deduplication merger
is used, which performs 1:1 deduplication
for samples. When set to penalty, penalty
based deduplication algorithm will be used.
At least one replica label has to be set via
--deduplication.replica-label flag.
--deduplication.replica-label=DEDUPLICATION.REPLICA-LABEL ...
Label to treat as a replica indicator of blocks
that can be deduplicated (repeated flag). This
will merge multiple replica blocks into one.
This process is irreversible.Experimental.
When one or more labels are set, compactor
will ignore the given labels so that vertical
compaction can merge the blocks.Please note
that by default this uses a NAIVE algorithm
for merging which works well for deduplication
of blocks with **precisely the same samples**
like produced by Receiver replication.If you
need a different deduplication algorithm (e.g
one that works well with Prometheus replicas),
please set it via --deduplication.func.
--delete-delay=48h Time before a block marked for deletion is
deleted from bucket. If delete-delay is non
zero, blocks will be marked for deletion and
compactor component will delete blocks marked
for deletion from the bucket. If delete-delay
is 0, blocks will be deleted straight away.
Note that deleting blocks immediately can cause
query failures, if store gateway still has the
block loaded, or compactor is ignoring the
deletion because it's compacting the block at
the same time.
--disable-admin-operations
Disable UI/API admin operations like marking
blocks for deletion and no compaction.
--downsample.concurrency=1
Number of goroutines to use when downsampling
blocks.
--downsampling.disable Disables downsampling. This is not recommended
as querying long time ranges without
non-downsampled data is not efficient and useful
e.g it is not possible to render all samples for
a human eye anyway
--enable-auto-gomemlimit Enable go runtime to automatically limit memory
consumption.
--hash-func= Specify which hash function to use when
calculating the hashes of produced files.
If no function has been specified, it does not
happen. This permits avoiding downloading some
files twice albeit at some performance cost.
Possible values are: "", "SHA256".
-h, --help Show context-sensitive help (also try
--help-long and --help-man).
--http-address="0.0.0.0:10902"
Listen host:port for HTTP endpoints.
--http-grace-period=2m Time to wait after an interrupt received for
HTTP Server.
--http.config="" [EXPERIMENTAL] Path to the configuration file
that can enable TLS or authentication for all
HTTP endpoints.
--log.format=logfmt Log format to use. Possible options: logfmt or
json.
--log.level=info Log filtering level.
--max-time=9999-12-31T23:59:59Z
End of time range limit to compact.
Thanos Compactor will compact only blocks,
which happened earlier than this value. Option
can be a constant time in RFC3339 format or time
duration relative to current time, such as -1d
or 2h45m. Valid duration units are ms, s, m, h,
d, w, y.
--min-time=0000-01-01T00:00:00Z
Start of time range limit to compact.
Thanos Compactor will compact only blocks, which
happened later than this value. Option can be a
constant time in RFC3339 format or time duration
relative to current time, such as -1d or 2h45m.
Valid duration units are ms, s, m, h, d, w, y.
--objstore.config=<content>
Alternative to 'objstore.config-file'
flag (mutually exclusive). Content of
YAML file that contains object store
configuration. See format details:
https://thanos.io/tip/thanos/storage.md/#configuration
--objstore.config-file=<file-path>
Path to YAML file that contains object
store configuration. See format details:
https://thanos.io/tip/thanos/storage.md/#configuration
--retention.resolution-1h=0d
How long to retain samples of resolution 2 (1
hour) in bucket. Setting this to 0d will retain
samples of this resolution forever
--retention.resolution-5m=0d
How long to retain samples of resolution 1 (5
minutes) in bucket. Setting this to 0d will
retain samples of this resolution forever
--retention.resolution-raw=0d
How long to retain raw samples in bucket.
Setting this to 0d will retain samples of this
resolution forever
--selector.relabel-config=<content>
Alternative to 'selector.relabel-config-file'
flag (mutually exclusive). Content of YAML
file with relabeling configuration that allows
selecting blocks to act on based on their
external labels. It follows thanos sharding
relabel-config syntax. For format details see:
https://thanos.io/tip/thanos/sharding.md/#relabelling
--selector.relabel-config-file=<file-path>
Path to YAML file with relabeling
configuration that allows selecting blocks
to act on based on their external labels.
It follows thanos sharding relabel-config
syntax. For format details see:
https://thanos.io/tip/thanos/sharding.md/#relabelling
--tracing.config=<content>
Alternative to 'tracing.config-file' flag
(mutually exclusive). Content of YAML file
with tracing configuration. See format details:
https://thanos.io/tip/thanos/tracing.md/#configuration
--tracing.config-file=<file-path>
Path to YAML file with tracing
configuration. See format details:
https://thanos.io/tip/thanos/tracing.md/#configuration
--version Show application version.
-w, --wait Do not exit after all compactions have been
processed and wait for new work.
--wait-interval=5m Wait interval between consecutive compaction
runs and bucket refreshes. Only works when
--wait flag specified.
--web.disable Disable Block Viewer UI.
--web.disable-cors Whether to disable CORS headers to be set by
Thanos. By default Thanos sets CORS headers to
be allowed by all.
--web.external-prefix="" Static prefix for all HTML links and redirect
URLs in the bucket web UI interface.
Actual endpoints are still served on / or the
web.route-prefix. This allows thanos bucket
web UI to be served behind a reverse proxy that
strips a URL sub-path.
--web.prefix-header="" Name of HTTP request header used for dynamic
prefixing of UI links and redirects.
This option is ignored if web.external-prefix
argument is set. Security risk: enable
this option only if a reverse proxy in
front of thanos is resetting the header.
The --web.prefix-header=X-Forwarded-Prefix
option can be useful, for example, if Thanos
UI is served via Traefik reverse proxy with
PathPrefixStrip option enabled, which sends the
stripped prefix value in X-Forwarded-Prefix
header. This allows thanos UI to be served on a
sub-path.
--web.route-prefix="" Prefix for API and UI endpoints. This allows
thanos UI to be served on a sub-path. This
option is analogous to --web.route-prefix of
Prometheus.
Found a typo, inconsistency or missing information in our docs? Help us to improve Thanos documentation by proposing a fix on GitHub here ❤️